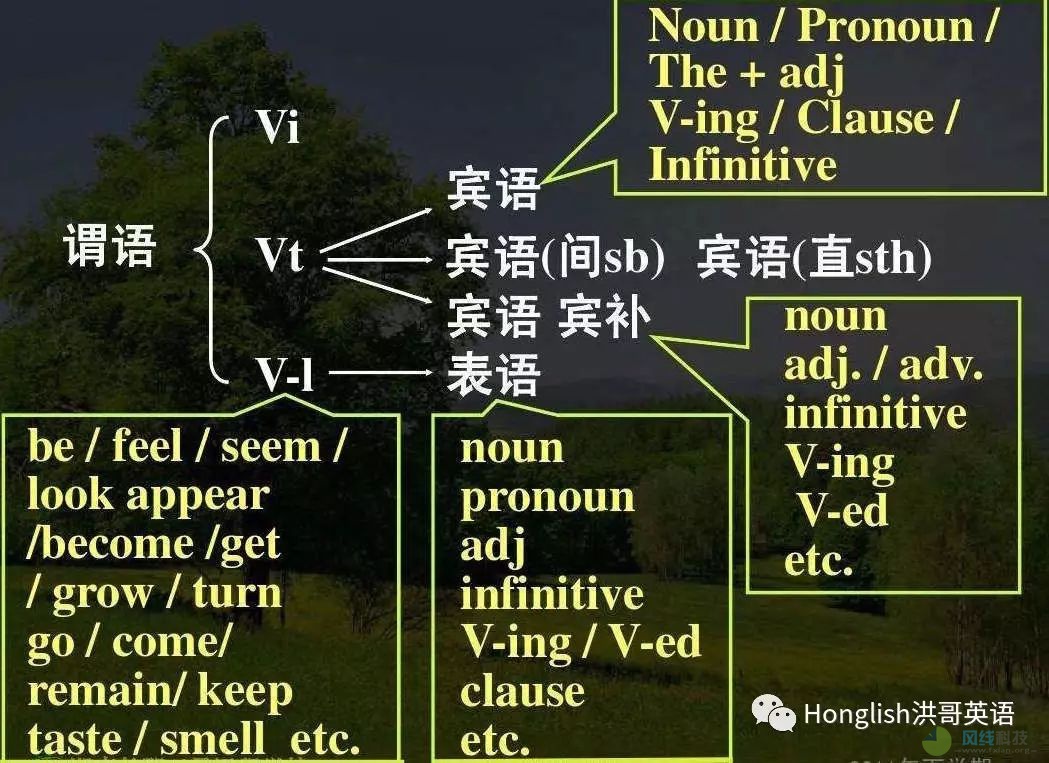
句子成分的定义:构成句子的各个部分叫做句子成分。句子成分有主要成分和次要成分;主要成分有主语和谓语;次要成分有表语、宾语、定语、状语、补足语和同位语。
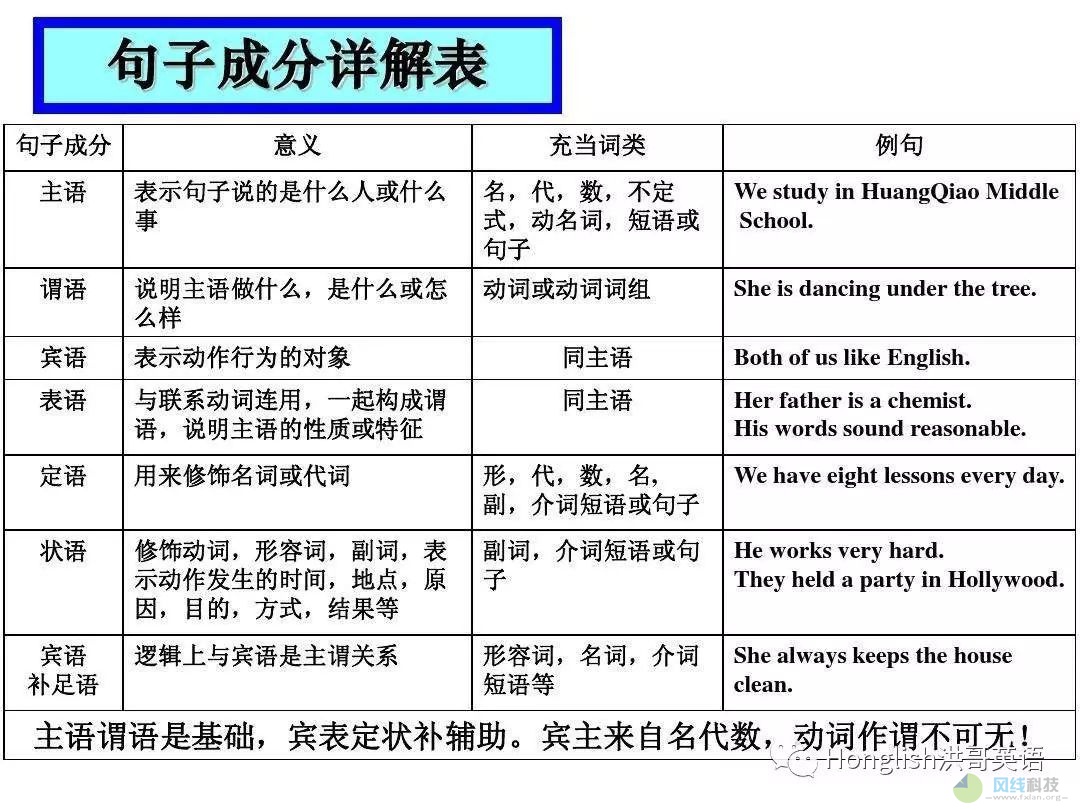
1. 主语
句子一般要有主语。在简单句中,主语一般由名词、代词、动名词或动词不定式(短语) 来充当。动名词、动词不定式作主语时通常用 it 作形式主语。
■名词作主语
English is very important. 英语是很重要的。
The students all love their Englishteacher. 这些学生都爱他们的英语老师。
■代词作主语
They go to school by bus. 他们乘公共汽车上学。
Most of the students come from thecountryside. 大多数学生来自农村。
■动名词作主语
Watching TV too much is bad for your eyes. 看电视太多对你的眼睛是有害的。
It’s no use regretting it. 后悔是无用的。
■动词不定式(短语)作主语
To see is to believe. 眼见为实。
It is very hard to get to sleep. 入睡很难。
2. 谓语
谓语必须由动词充当,但动词不定式、动名词、分词为非谓语动词不能作谓语。可作谓语的动词一般为行为动词(表动作)和连系动词(表状态),行为动词根据其后是否可直接接宾语,又可分为及物动词和不及物动词。
■及物动词作谓语
We shouldhelp each other. 我们应该互相帮助。
They respectone another. 他们互相尊重(对方)。
All ofthe students like the novel. 所有这些学生都喜欢这本小说。
Did yousee many people there? 你在那儿看见许多人了吗?
■不及物动词作谓语
He lefthere yesterday. 他昨天离开这儿。
You’redriving too fast. 你开车开得太快了。
Theteacher came in, book in hand. 老师走进教室,手里拿着书。
He wentabroad in the September of 1988. 他于1988年9月出国。
■连系动词表状态
He is anexcellent teacher. 他是位优秀的教师。
Her sonis a friend of ours. 她的儿子是我们的朋友。
Ours is agreat country. 我们的国家是一个伟大的国家。
The boxitself is not so heavy. 箱子本身并不重。
3. 表语
表语与连系动词连用,构成系表结构,说明主语的身份或特征,一般由形容词、名词、动名词、动词不定式、分词等充当。如:
They arebrother and sister. 他们是兄妹。
What Iwant to say is this. 我想说的就是这点。
Herfather is sixty-five. 她父亲65岁。
John iscaptain of the team. 约翰是足球队的队长。
The poorboy was myself. 那个可怜的孩子就是我自己。
The oneswho really want it are ourselves. 真正想要它的是我们自己。
All youneed do is to take a taxi from the airport. 你只需从机场打个的即可。
My favourite sport is swimming. 我最喜爱的运动是游泳。
4. 宾语
宾语是行为动作的对象,一般可分为动词宾语和介词宾语,充当宾语的可以是名词、代词、动名词、动词不定式或整个句子。如:
I likeChinese food. 我喜欢中国菜。
I boughta ticket for Milan. 我买了一张去米兰的车票。
I enjoyedtalking to you. 我和你谈话很高兴。
Have youfinished dressing? 你衣服穿好了吗?
Hecertainly did not want to join them. 他确实不想参加他们的活动。
Theydecided to close the border. 他们决定封闭边境。
We hopedthat all would come well. 我们希望一切都会好转。
Weexpected that you would stay for a few days. 我们预计你会待几天的。
5. 定语
定语为句子的次要成分,起修饰限制名词或代词的作用,可分为前置定语和后置定语。一般由形容词性物主代词、数词、形容词、副词、介词短语、动词不定式、分词(短语) 或句子充当。
His father is a doctor. 他父亲是一名医生。
Mr. Green has two sons. 格林先生有两个儿子。
The girl under the tree is Kate. 在树底下的那个女孩是凯特。
The man downstairs couldn’t sleep well. 楼下的那个人不能睡好觉。
I bought a new dictionary. 我买了本新字典。
Can you find out the answer to the question?你能找到这个问题的答案吗?
Would you like something to drink? 你想要些喝的东西吗?
A barking dog seldom bites. 吠狗很少咬人。
A man going to die is always kind-hearted. 人之将死,其言也善。
The suggestion sent to the committee wasadopted. 送往委员会的建议被采纳了。
Do you know the man who is standing next toMr. Green? 你认识站在格林先生旁边的那个人吗?
6. 状语
英语中的状语用来修饰动词、形容词或副词,主要由副词、介词短语、动词不定式、分词充当,或由连词引导状语从句,表示时间、地点、程度、目的、方式,比较、让步、条件、原因、结果、伴随等。
(1) 时间状语
I often get up at 5:30 in the morning. 我常常在早上5:30起床。
Hearing the news, they felt very excited. 听到这个消息,他们感到很兴奋。
Go along this street until you reach theend. 沿着这条街走直到到达尽头为止。
(2) 地点状语
Pandas only live in China. 熊猫仅生活在中国。
You should put the book where it was. 你应该把这本书放回原来的地方。
(3) 程度状语
I have quite a lot of work to do. 我有相当多的工作要做。
(4) 目的状语
We’ll go to the beach for a picnic thisSunday. 这个星期天我们将去沙滩野炊。
He took some change from his pocket to buya newspaper. 他从口袋里掏出一些零钱来买报纸。
She got up early so that she could catchthe first bus. 她早早地起床,以便能够赶上这辆早班车。
(5) 方式状语
We usually go to school on foot. 我们通常步行去上学。
Please do it as I told you. 请按我告诉你的去做。
(6) 让步状语
Though she has a lot of money, she isunhappy. 虽然她很有钱,而她并不幸福。
No matter what happens, I will never loseheart. 无论发生什么,我将决不失去信心。
(7) 条件状语
If you don’t work hard, you’ll fall behindthe others. 假如你不努力学习,你将落后于别人。
Given more attention, the flowers wouldhave grown better. 如果给予更多的关心的话,这些花将长得更好。
(8) 比较状语
Your watch is not the same as mine. 你的手表与我的不一样。
Mike is not as (so) tall as Jack. 迈克不及杰克高。
(9) 原因状语
We didn’t go to the park because of the badweather. 由于天气不好,我们没有去公园。
I’m glad to meet you. 见到你我很高兴。
Being ill, he didn’t go to school. 由于病了,他没有去上学。
(10) 结果状语
The wind was so strong that we could hardlymove forward. 风是如此地猛烈,以致于我们寸步难行。
He left early, so that he caught the train.他早早地离去,(结果) 因此赶上了火车。
(11) 伴随状语
The doctor hurried off, with a medicine boxunder his arm. 这位医生匆匆离去,胳膊下夹着一个药箱子。
The teacher came into the classroom,followed by a group of his students. 老师进到教室里来,后面跟着一群学生。
7. 宾语补足语
宾语补足语主要用来补充说明宾语,与宾语之间存在逻辑上的主谓关系或动宾关系,可由名词、形容词、动词不定式、分词等充当。如:
Tom foundthe climb quite easy. 汤姆觉得爬山很容易。
Don’t beso formal. Call me Jim. 不要这样正规,叫我吉姆好了。
I’mfinished. Let’s go now. 我已干完,咱们走吧。
You mustkeep it clean. 你要把它保持干净。
I havethe car waiting. 我让汽车等着。
We hadthe machine repaired. 我们请人修理了机器。
Why don’tyou have your hair cut? 你为什么不理发?
He hadhis finger cut. 他的手指弄伤了。
I had mywatch stolen yesterday. 我的表昨天被人偷去了。
I have alot of work to do. 我有许多工作要做。
She hasplenty of clothes to wear. 她有足够的衣服穿。
He mademe repeat the story. 他要我把那事重讲一遍。
Rainmakes plants grow. 雨水使植物生长。
注意:后跟名词作宾语补足语的动词有 call, name, think, make, choose等,后跟形容词作宾语补足语的谓语动词有 keep, find, get, think,make 等。动词不定式作宾语补足语时,当谓语动词为感官动词(如 feel, see, hear, notice, watch,observe, listen to, look at 等),使役动词(如 let, have, make 等),动词不定式不带 to。